Risks Management
In order for the SDC's concern to achieve its goals within the framework of reducing the risks of dealing in securities and out of the belief in the importance of finding and applying technical and legal methods and standards to manage the risks of operations related to all tasks entrusted to the SDC with the utmost levels of accuracy, safety and reliability and in harmony with international standards and the best practices concerned with risk management. To achieve these goals, the SDC has asserted a set of policies, strategies and procedures, which together represent the risk management processes.
The concept of risks
Risks are potential events characterized by a state of uncertainty that affect the achievement of objectives. They may cause a fundamental change in the timeframe, cost, quality, etc.. Their impact can be positive or negative depending on the mechanism for dealing with them. Risks are divided according to their source:
Internal risks (preventive, re-active):
Preventive: can be controlled before they occur through binding procedures and controls.
Re-active: can be dealt with after they occur using pre-established treatment plans.
External risks: are sudden events with a major impact that cannot be controlled, but can be dealt with and an attempt can be made to cope with them as much as possible within pre-established emergency plans.
Risk management is an ongoing process that aims to identify, classify, analyze, evaluate, and control potential risks in order to control the consequences of their occurrence by reducing their negative effects on the SDC and trying to benefit from available opportunities in a sound scientific manner within a set of policies, strategies, and procedures. Risk management can be divided into two levels:
Risk management at the operational level: It is related to daily routine operational processes, and is managed by departments in coordination with the risk management unit at the SDC, and its impact is specific and controllable.
Risk management at the strategic level: It is directly related to senior management, the board of directors, and the decisions emanating from them, and is related to the SDC's strategic objectives and affects their achievement.
Risk management policy and general principle
The risk management policy at the SDC stems from its vision, mission, and objectives of enhancing investor confidence in securities and reducing risks related to the settlement of trading transactions executed through the market. It is consistent and integrated with the SDC’s culture and core values that policy emerged and from that all decisions and strategies related to managing the SDC’s risks.
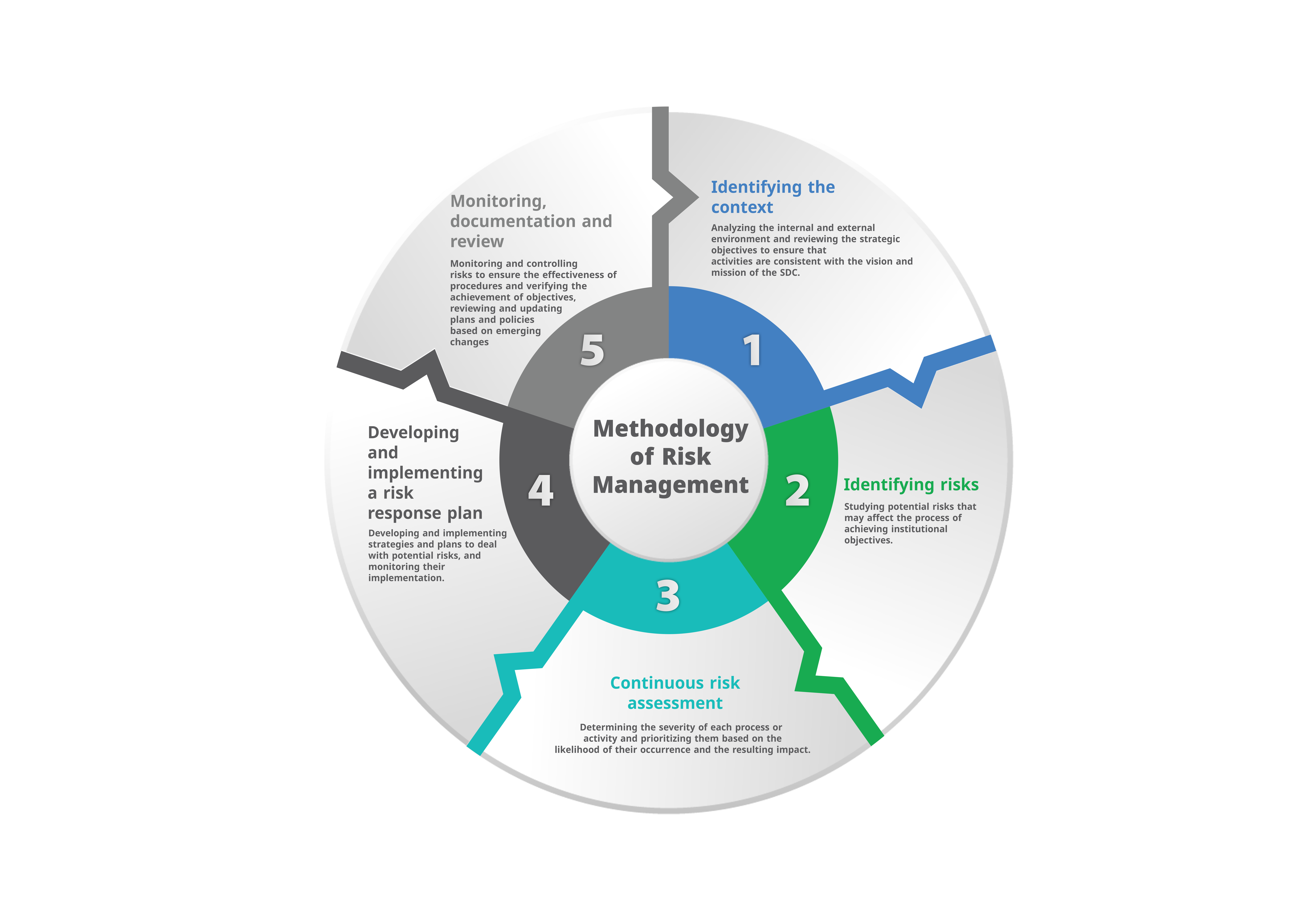
Methodology of Risk Management
The SDC's risk management methodology includes a clear mechanism that is compatible with the best international practices concerned with risk management and in harmony with the essence of (ISO 31000) standards. This methodology includes procedures needed to deal with potential risks, and usage of tools and standards to measure and evaluate the effectiveness of risk management, and identify the events likely to be encountered during the applying the risk management strategies at the SDC.
This methodology consists of the following steps:
- Identifying the context: Analyzing the internal and external environment and reviewing the strategic objectives to ensure that activities are consistent with the vision and mission of the SDC.
- Identifying risks: Studying potential risks that may affect the process of achieving institutional objectives.
- Continuous risk assessment: Determining the severity of each process or activity and prioritizing them based on the likelihood of their occurrence and the resulting impact.
- Developing and implementing a risk response plan: Developing and implementing strategies and plans to deal with potential risks, and monitoring their implementation.
- Monitoring, documentation and review: Monitoring and controlling risks to ensure the effectiveness of procedures and verifying the achievement of objectives, reviewing and updating plans and policies based on emerging changes.
The basic pillar for the success of the risk management process
The basic pillar for the success of the risk management process begins with the continuous encouragement to adopt a risk management culture, enhancing awareness of its importance, and involving the risk management unit in important activities, functions, and the decision-making process. This aims to make comprehensive decisions that consider the challenges and opportunities associated with these decisions, which contributes to developing a clear understanding of the events that the SDC may be exposed to and that may result in potential risks.
General Principle for Risk management Policy
The basic principle on which the SDC's risk management policy is based stems from the fact that the SDC is a public utility institution established under the Securities Law, and does not aim to make a profit. Therefore, all operational risks associated with the tasks assigned to the SDC must be avoided. Since it is known that not all risks can be completely eliminated, the impact of some less important types of risks can be accepted or reduced based on measuring the degree of potential risk versus the cost of completely avoiding it.
Strategies and responsibilities
Risk management in the SDC forms one of the basic elements of the SDC’s strategies. So that a comprehensive framework is developed to integrate, design, evaluate and improve the response to the potential risks that could affect the operational transactions of tasks assigned to the SDC with the utmost accuracy, safety and reliability in accordance with international standards and best practices. In order to achieve this, the SDC adopts the following strategies:
Develop effective frameworks and policies: to deal with financial, operational, legal and technological risks.
Integrated management: is considered an integral part of all organizational activities at the SDC, involves all stakeholders and is adopted as a comprehensive risk management effort.
Commitment to comprehensive cooperation in risk management: including the opinions and perceptions of stakeholders, to increase awareness of risks and predict them in accordance with changes and developments.
A dynamic response to variables: in the internal and external context of the SDC’s environment is achieved by providing evidence-based and fact-based information, ensuring its updating, accuracy and timely access. Risks are dealt with and responded to as follows:
- Risk Control: Implementing controls and precautionary measures to reduce the impact and likelihood of negative risks and ensure they remain within acceptable levels.
- Risk Avoidance: Developing preventive and re-active plans to deal with or eliminate the causes of negative risks.
- Risk Acceptance/Tolerance: Accepting risks if their consequences can be borne to obtain positive results in the long term, or if they cannot be avoided with re-active plans and have become a reality and the costs of treating them are much higher than bearing them.
- Risk Transfer: Transferring risks to another party to avoid their consequences, which requires paying a fee to bear these risks.
Responsibilities:
Establishing a risk management policy is one of the authorities of the Board of Directors, which is also responsible for approving the strategy and identify the degree of risk, as well as the annual review or whenever the need arises. While the Executive Management is responsible for implementing and planning risk management activities at the SDC.
Their duties are as follows:
First: The role of the executive management
- Follow up on the implementation of the annual risk management plan: Involve the SDC's departments in identifying the risks that fall within their responsibilities, and provide the risk management unit with continuous updates and information about them.
- Proactively deal with risks: Proactively highlight emerging risks and develop plans to address them after analyzing and evaluating them.
- Re-evaluate risks: Continuously monitor the risk assessment after starting to implement the prepared plans.
- Disseminate and adopt a risk management culture: Enhance employees' awareness of the importance of risk management and encourage them to adopt this culture.
Second: The role of the Risk Management Unit
- Studying potential risks: identifying, analyzing and evaluating risks, developing plans and policies necessary to deal with them, and monitoring, observing and reviewing any developments that may arise.
- Protecting the SDC: increasing awareness of the opportunities and threats that the SDC may face, to seize opportunities and avoid threats.
- Increasing awareness of the consequences of risks: Raising awareness of the SDC's departments about the consequences of risks that may fall within their responsibilities, and enhancing mechanisms for dealing with them.
Learned lessons and improvement
The SDC is committed to providing a safe and reliable environment for investors that guarantee the safekeeping, transfer of ownership of securities and the settlement of their prices by adopting international standards and best practices, as well as maintaining the confidentiality of information. The process of risk management is an essential part of our vision to achieve excellence in our services and maintain our reputation as a reliable and attractive Central Securities Depository for securities investments.
SDC’s policy ensures continuous communication and consultation with stakeholders throughout the risk management process, as well as continuous monitoring, controlling, and reviewing for every risk, and learning from the experiences of others and lessons learned plays a major role in the continuous improvement of risk management at the SDC.
Risk management aspects
The following is the most prominent aspects of risk management in the SDC:
Legislations
Integrated legislations: The SDC relies on an integrated system of legislation that includes internal by-laws, instructions, executive procedures, and policies, which ensures the identification of precise terms and provisions for implementing its administrative, financial, and technical operations.
Continuous review: The SDC continuously reviews legislation to keep pace with developments related to its business and services, as well as developments in the capital market. Feedback is collected from capital market institutions and target groups of any legislative amendments, including public shareholding companies and financial services companies (financial brokers and custodians).
Updating Legislation: Legislation is amended to reflect the changing needs of the market and members, while adhering to risk management principles and international standards adopted in this field.
Safekeeping, classification and security of information and data
Maintained the registers electronically: All records of securities owners are kept on the SDC’s electronic system (SCORPIO) and held in book-entry (dematerialized form). The SDC’s electronic system includes an integrated system of permissions for users on the system’s screens and reports. These permissions are granted according to the needs and requirements of the work to ensure the safety and security of data and information and the integrity of records.
Data Center Management: Establishing, operating and managing three data centers to ensure reducing risks related to the availability, integrity and continuity of information in emergency situations, which contributes to facilitating the immediate recovery of complete system and service data.
Implementation of the Business Continuity & Disaster Recovery Plan: The SDC conducts periodic tests in cooperation with its members to examine the readiness of business continuity & Disaster Recovery sites.
Providing advanced security and protection systems: The SDC uses advanced systems to protect and monitor electronic systems and communication networks to ensure information security and the continuity of business and services without interruption.
Classification of registers: registers are classified in accordance with their nature and legislative organization into confidential data, statistical data, and aggregate data, while adhering to data confidentiality and reducing any risks related to information confidentiality.
Coordination with the National Cyber Security Center: The SDC cooperates with the National Cyber Security Center to obtain technical security services that ensure the protection and enhancement of the integrity and availability of information and data, and reduce any risks in this regard.
Safekeeping, registration, and transferring the ownership of securities
Establishing a database for issuers: The SDC organizes a comprehensive database for all issuers of securities within its electronic system, which ensures the registration and safekeeping of ownership of securities transparently in the Kingdom’s stock market.
Identifying the investor with the unified investor number (SDC number): This number has been approved to prevent any confusion, especially regarding the similarity of names. As for the reference number, which is used for trading purposes only, it is the number given to the investor by the broker for trading purposes and linked to the SDC number, so every investor can deal with any number of brokers by obtaining a reference number for trading purposes from each broker and all these reference numbers remain linked to only one SDC number consisting of ten digits.
Applying the principle (Know Your Customer-KYC): The SDC is committed to the policies and procedures of anti-money laundering and anti-terrorism policies and procedures used to determine the true identity of the customer, through applying the “Know Your Customer” (KYC) principle by exerting the due diligence to determine the true identity of the customer, and verifying that investors are not linked to the national list of money laundering and terrorist financing, or to the lists issued by the penalties’ committees of the Security Council- United Nations.
Clearing and Settlement
Settlement Guarantee Fund Management: The SDC manages the Fund that was established in accordance with the provisions of the Securities Law as a financially independent legal entity to ensure coverage of the cash deficit and deficits in the securities account of a Fund member in connection with his sales of securities on the market.
Electronic linkage with the Stock Exchange: The electronic linking between the SDC’s systems and the stock exchange’s trading system through an electronic system called the Central Control System (CCM) with the aim of improving the technical environment of capital market institutions by controlling trading operations and reducing the risks associated with those operations (Order Verification).
Linking with the Real Time Gross Settlement System (RTGS): The electronic SDC system has been linked with the Real Time Gross Settlement System through the global SWIFT network in order to receive and send for the settlement of securities prices using the latest means in the field of linking and exchanging messages and information with all banks (MX messages – ISO 20022).
Developing a comprehensive emergency plan: The SDC develops and updates a comprehensive emergency plan that ensures the continuity of its operations in all circumstances. This plan includes an analysis of risks and potential problems to establish a preventive strategy to avoid risks and disasters and to cope with them in case they occur, in accordance with international standards and best practices.
Strict procedures for defaulting brokers: The SDC imposes strict procedures on brokers who do not commit to paying the amounts due for settlement as of day T+1, including suspension of trading to reduce risk and control them.
Buy in and Sell out measures: These procedures are applied to ensure that the sold security is delivered in exchange for payment of its price.
Application of the Delivery versus Payment (DvP) principle: The SDC ensures that the sold security will not be delivered and its ownership transferred until its price has been paid, which enhances the security and reliability of trading operations.
Risk Management and Internal Control
The organizational structure of the SDC includes a Risk Management Unit and an Internal Audit Department, both of which are linked to the Board of Directors and are entrusted with the following tasks:
First: Risk Management Unit
- Identify, analyze and evaluate potential risks that the SDC may face.
- Develop and implement strategies and plans for risk management.
- Monitor, review and update plans and policies based on developments.
- Submit periodic reports to the Board of Directors on the status of risk management and the actions taken.
Second: Internal Audit Department
- Auditing all operations, activities and procedures in all financial, administrative and technical aspects.
- Ensuring that the SDC and its employees adhere to the specified standards and procedures, whether internal or external.
- Submitting periodic and annual supervisory reports to the audit committee emanating from the SDC Board of Directors to enable issuing the necessary recommendations and decisions to address any observations contained in those reports.